These case is refer to a Singaporean teenager which be the first person who charged under Singapore new law--Computer Misuse Act for tapping to gain unauthorized access into other's home WiFi. His neighbor has made a police report on this incident against him. If these incident convicted, he would be jail up to 3 years and fined up to Singapore Dollar $10,000.
As everybody know that stealing our's neighbor WiFi is an unethical things but why the teenager do so? Is it the applying and installation for Internet access fees is too high? Or the teenager just want to find some excitement? Does he think about the consequences before he take action?It's a funny thing, since he was not stealing anything tangible but still be charged under
In my opinion, owner have more responsibilities to secure the home WiFi system. Service provider can provide the service such as teach the owner about how to setup 'Security Enabled' wireless network to avoid other people unauthorized access into their home WiFi. The owner need to set a password while setup security-enabled wireless network and it was a kind of privacy for the owner which cannot be exposure to other included service provider. Besides, some of the owner did not set up a security-enabled wireless network and it could be automatically accessed by other. So, in these case the service provider does not held any responsibility to secure the home WiFi system. However, the owner his or her own/ manage the network is responsible for anything that happens on the network.
Do you think piggy-backing on the neighbour's connection is an unethical actions?
Some of the people think it is not only unethical, it is technically trespassing. In my opinion, if someone stealing their neighbour's connection but they will share the cost of service openly with their neighbours, it is consider ethical. 'Tacit' approval does not work neither as most open wireless networks are there as the owner is not technically aware. So, we should not use someone ignorance as a approval. Besides, some of the people open their networks but it doesn't mean they were a "free game". For instance, many business LAN networks can be accessed, if you just enter the building and plug in but you are still not paying for that service. So, if we want to piggy-backing our neighbour's wireless, we should ask them first before we using it and also tell them what we will be using it in order to avoid being sued by our neighbours.
Here are some steps on how to prevent and setup a secure home WiFi network.
Step 1: Before Beginning
- A wireless route
- Wireless adapter or a wireless-enabled laptop or desktop PC.

- A Broadband connection to the internet (typically via cable or DSL modem)
Ethernet Cable
• The IP address assigned to you system by your ISP (Internet Service Provider) if you use a static IP address.
• Username and password assigned to you by your ISP.
• The MAC address for all wireless network adapters.
Step 2: Preparing for the Installation Job
Before you start your installation, you need to know if your ISP provides a static IP address.
In Windows XP
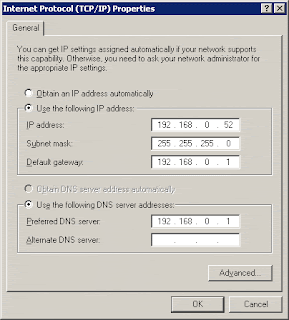
• Click Start – Settings – Control Panel – Network Connections – Local Area Connection – Properties – Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) – Properties.
In Windows
• Click Start – Control Panel – Network and
• Click Start – Programs – Accessories – Command Prompt
• A new text-only window opens. Type ipconfig/all and press Enter
• The numbers and letters listed on the line titled Physical Address is your MAC Address.
Step 3: Installing the Wireless Router
Disconnect Ethernet cable from PC and connect it to router's WAN port
Connect a second Ethernet cable from your PC's Ethernet port to one of the router's LAN ports.
Turn on the modem, wait until connects to the Internet (check the activity lights).
Plug in and power on the router and turn on your PC.
When Windows boots, open a browser window and try a few Web sites to test your Internet connection.
Step 4: Configuring the Router
Using the PC connected to the router, launch your browser. In the URL address field, enter the router configuration IP address provided in the router’s documentation. You will also need to enter the User Name and default password.
Jotted down an IP address, set the router to use a static IP address and enter the address and other information. Enter the username and password you selected to log on to your ISP. Leave other settings such as encryption and SSID at their defaults for now, exit your router's configuration routine, and check your Internet connection. If you can't access any Web sites, check your router's documentation for troubleshooting advice and call the manufacturer for technical support.
Step 5: Setting the Password
• Click TOOLS – ADMIN
• Enter a password for the administrator
• Click Save Settings
Step 6: Setting the Service Set Identifier (SSID)
• Click SETUP – WIRELESS – MANUAL SETUP
• Enter a new name for your network
• Click Save Settings
Step 7: Enable Encryption
• Select WPA-Personal Security Mode
• Enter a new Pre-Shared Key
• Click Save Settings
Step 8: Installing the Wireless Adapters
Laptop cards install in the card port. For desktop PCs, shut down your system, install the adapter (as shown following) and reboot. Note: If you have a PC with built-in Wi-FI you won’t need the PC card adaptor.
If you've followed our instructions faithfully, your network is now secure and you will need to enter your pass phrase to connect to the router with your wireless connections. Your computers will see your router, but lack the pass phrase to connect. Both Windows XP and














No comments:
Post a Comment